Spring Cloud Open Feign 源码速读
整体流程图
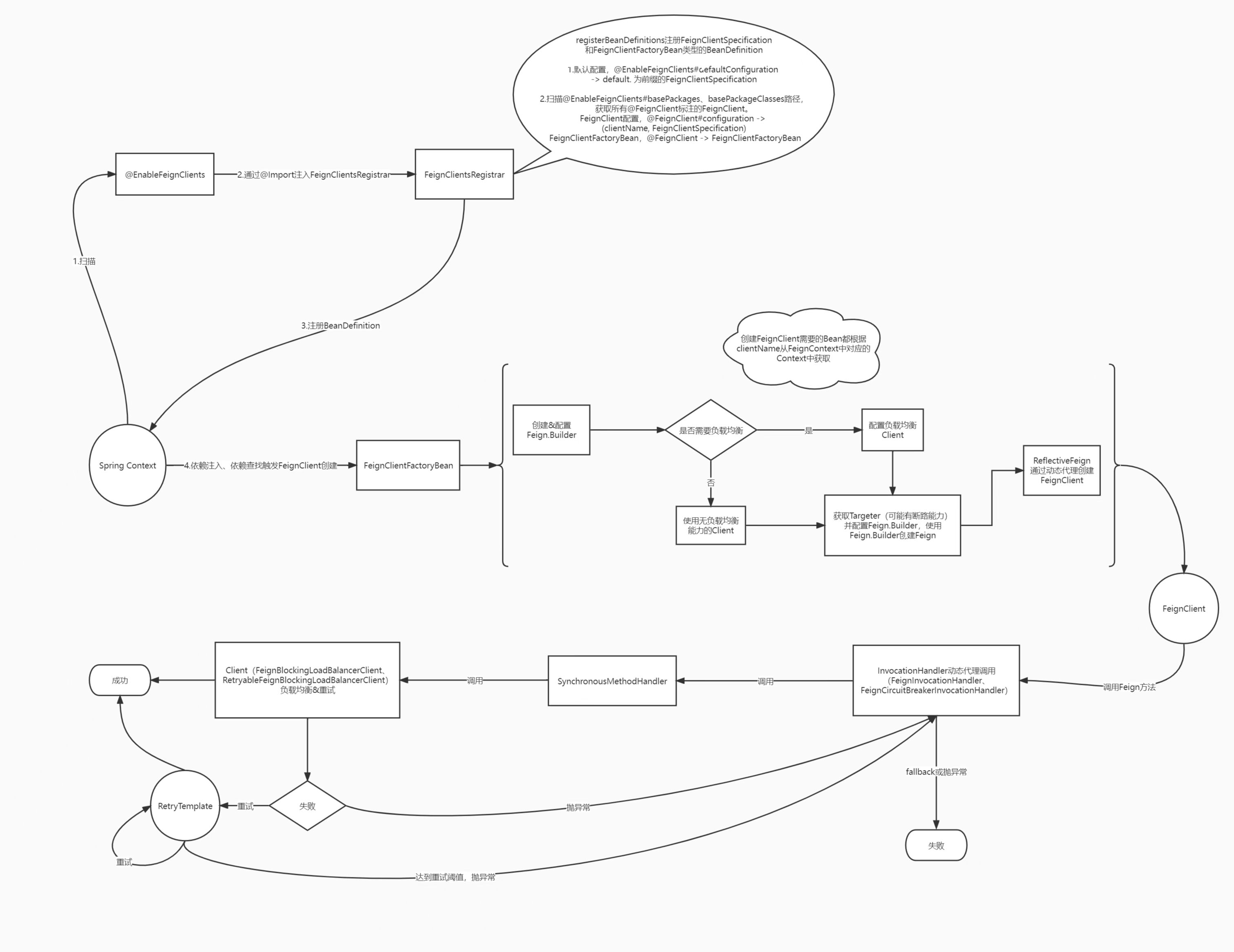
Feign BeanDefinition注入
@EnableFeignClients
进行一些配置,通过@Import注入FeignClientsRegistrar
FeignClientsRegistrar
注入BeanDefinition,包括@EnableFeignClients配置的全局FeignClientSpecification(name以default开头),@FeignClient配置的FeignClientSpecification(各个FeignClient级别)以及FeignClientFactoryBean
FeignClientSpecification
FeignClient配置规范,包含了FeignClient的name,以及配置类数组
FeignClient name优先级,@FeignClient#contextId > @FeignClient#name
FeignClientProperties
Feign配置文件对应实体类
FeignClientsConfiguration
FeignClient默认的配置,包含了Feign.Builder、Encoder、Decoder、FeignLogger等,会在FeignClientSpecification和配置文件缺省时自动注入
FeignAutoConfiguration
注入FeignContext、Targeter、Client等Bean
FeignClient 实例化
FeignContext
Feign配置隔离核心,继承NamedContextFactory<FeignClientSpecification>,NamedContextFactory#defaultConfigType为FeignClientsConfiguration
NamedContextFactory解析
以name创建不同的Context,以达到差异化配置的效果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
public abstract class NamedContextFactory<C extends NamedContextFactory.Specification>
implements DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware {
private final String propertySourceName;
private final String propertyName;
//name -> context map
private Map<String, AnnotationConfigApplicationContext> contexts = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//name -> 配置 map
private Map<String, C> configurations = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//所有context的parent
private ApplicationContext parent;
//默认的配置类
private Class<?> defaultConfigType;
public NamedContextFactory(Class<?> defaultConfigType, String propertySourceName, String propertyName) {
this.defaultConfigType = defaultConfigType;
this.propertySourceName = propertySourceName;
this.propertyName = propertyName;
}
//......
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext getContext(String name) {
//根据name获取context,典型的map获取创建
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
synchronized (this.contexts) {
if (!this.contexts.containsKey(name)) {
this.contexts.put(name, createContext(name));
}
}
}
return this.contexts.get(name);
}
//创建context
protected AnnotationConfigApplicationContext createContext(String name) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context;
if (this.parent != null) {
// jdk11 issue
// https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-netflix/issues/3101
// https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-openfeign/issues/475
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
if (parent instanceof ConfigurableApplicationContext) {
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(
((ConfigurableApplicationContext) parent).getBeanFactory().getBeanClassLoader());
}
else {
beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader(parent.getClassLoader());
}
context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(beanFactory);
context.setClassLoader(this.parent.getClassLoader());
}
else {
context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
}
if (this.configurations.containsKey(name)) {
//注入名字获取到的配置
for (Class<?> configuration : this.configurations.get(name).getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
for (Map.Entry<String, C> entry : this.configurations.entrySet()) {
//注入default.开头的默认配置
if (entry.getKey().startsWith("default.")) {
for (Class<?> configuration : entry.getValue().getConfiguration()) {
context.register(configuration);
}
}
}
//注入PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration(开启占位符解析),以及默认的配置
context.register(PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration.class, this.defaultConfigType);
context.getEnvironment().getPropertySources().addFirst(new MapPropertySource(this.propertySourceName,
Collections.<String, Object>singletonMap(this.propertyName, name)));
if (this.parent != null) {
// Uses Environment from parent as well as beans
context.setParent(this.parent);
}
context.setDisplayName(generateDisplayName(name));
context.refresh();
return context;
}
protected String generateDisplayName(String name) {
return this.getClass().getSimpleName() + "-" + name;
}
//获取Bean,先根据name获取对应的context,然后在从context中获取Bean,下面的方法都差不多
public <T> T getInstance(String name, Class<T> type) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = getContext(name);
try {
return context.getBean(type);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException e) {
// ignore
}
return null;
}
public <T> ObjectProvider<T> getLazyProvider(String name, Class<T> type) {
return new ClientFactoryObjectProvider<>(this, name, type);
}
public <T> ObjectProvider<T> getProvider(String name, Class<T> type) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = getContext(name);
return context.getBeanProvider(type);
}
public <T> T getInstance(String name, Class<?> clazz, Class<?>... generics) {
ResolvableType type = ResolvableType.forClassWithGenerics(clazz, generics);
return getInstance(name, type);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getInstance(String name, ResolvableType type) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = getContext(name);
String[] beanNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(context, type);
if (beanNames.length > 0) {
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (context.isTypeMatch(beanName, type)) {
return (T) context.getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
return null;
}
public <T> Map<String, T> getInstances(String name, Class<T> type) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = getContext(name);
return BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, type);
}
/**
* Specification with name and configuration.
*/
public interface Specification {
String getName();
Class<?>[] getConfiguration();
}
}
FeignClientFactoryBean
主要看getTarget() 方法,使用FeignContext获取Feign.Builder,并进行配置,Feign的配置来源于配置文件和@FeignClient、@EnableFeignClients以及默认配置类,根据FeignClientProperties#defaultToProperties可以控制配置文件以及代码配置的优先级。配置主要包括Encoder、Decoder、ErrorDecoder、Contract等。其中负载均衡与否是根据配置的url进行判断后选择对应的Client。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
<T> T getTarget() {
FeignContext context = beanFactory != null ? beanFactory.getBean(FeignContext.class)
: applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class);
Feign.Builder builder = feign(context);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(url)) {
if (LOG.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOG.info("For '" + name + "' URL not provided. Will try picking an instance via load-balancing.");
}
if (!name.startsWith("http")) {
url = "http://" + name;
}
else {
url = name;
}
url += cleanPath();
//负载均衡配置
return (T) loadBalance(builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(type, name, url));
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(url) && !url.startsWith("http")) {
url = "http://" + url;
}
String url = this.url + cleanPath();
Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class);
if (client != null) {
//无需负载均衡使用client.getDelegate()的client配置
if (client instanceof FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) {
// not load balancing because we have a url,
// but Spring Cloud LoadBalancer is on the classpath, so unwrap
client = ((FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) client).getDelegate();
}
if (client instanceof RetryableFeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) {
// not load balancing because we have a url,
// but Spring Cloud LoadBalancer is on the classpath, so unwrap
client = ((RetryableFeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) client).getDelegate();
}
builder.client(client);
}
applyBuildCustomizers(context, builder);
Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class);
return (T) targeter.target(this, builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(type, name, url));
}
protected <T> T loadBalance(Feign.Builder builder, FeignContext context, HardCodedTarget<T> target) {
Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class);
if (client != null) {
builder.client(client);
applyBuildCustomizers(context, builder);
Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class);
return targeter.target(this, builder, context, target);
}
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No Feign Client for loadBalancing defined. Did you forget to include spring-cloud-starter-loadbalancer?");
}
在配置完Client后会用Targeter获取最终的FeignClient代理对象,而断路的配置也是在有断路能力的Targeter中配置的。
FeignCircuitBreakerTargeter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
class FeignCircuitBreakerTargeter implements Targeter {
//断路工厂接口,具体实现可以用Resilience4j、ribbon、Sentinel等,存在这个Bean才会注入FeignCircuitBreakerTargeter见FeignAutoConfiguration
private final CircuitBreakerFactory circuitBreakerFactory;
private final boolean circuitBreakerGroupEnabled;
private final CircuitBreakerNameResolver circuitBreakerNameResolver;
......
@Override
public <T> T target(FeignClientFactoryBean factory, Feign.Builder feign, FeignContext context,
Target.HardCodedTarget<T> target) {
if (!(feign instanceof FeignCircuitBreaker.Builder)) {
//断路能力判断,用Feign.Builder#target获取Feign代理对象
return feign.target(target);
}
FeignCircuitBreaker.Builder builder = (FeignCircuitBreaker.Builder) feign;
String name = !StringUtils.hasText(factory.getContextId()) ? factory.getName() : factory.getContextId();
Class<?> fallback = factory.getFallback();
if (fallback != void.class) {
return targetWithFallback(name, context, target, builder, fallback);
}
Class<?> fallbackFactory = factory.getFallbackFactory();
if (fallbackFactory != void.class) {
return targetWithFallbackFactory(name, context, target, builder, fallbackFactory);
}
return builder(name, builder).target(target);
}
//fallbackFactory代理
private <T> T targetWithFallbackFactory(String feignClientName, FeignContext context,
Target.HardCodedTarget<T> target, FeignCircuitBreaker.Builder builder, Class<?> fallbackFactoryClass) {
FallbackFactory<? extends T> fallbackFactory = (FallbackFactory<? extends T>) getFromContext("fallbackFactory",
feignClientName, context, fallbackFactoryClass, FallbackFactory.class);
//配置完后用Feign.Builder#target获取Feign代理对象
return builder(feignClientName, builder).target(target, fallbackFactory);
}
//fallback代理
private <T> T targetWithFallback(String feignClientName, FeignContext context, Target.HardCodedTarget<T> target,
FeignCircuitBreaker.Builder builder, Class<?> fallback) {
T fallbackInstance = getFromContext("fallback", feignClientName, context, fallback, target.type());
//配置完后用Feign.Builder#target获取Feign代理对象
return builder(feignClientName, builder).target(target, fallbackInstance);
}
private <T> T getFromContext(String fallbackMechanism, String feignClientName, FeignContext context,
Class<?> beanType, Class<T> targetType) {
//从FeignContext中获取fallback或fallbackFactory
Object fallbackInstance = context.getInstance(feignClientName, beanType);
......
return (T) fallbackInstance;
}
//Feign.Builder断路配置
private FeignCircuitBreaker.Builder builder(String feignClientName, FeignCircuitBreaker.Builder builder) {
return builder.circuitBreakerFactory(circuitBreakerFactory).feignClientName(feignClientName)
.circuitBreakerGroupEnabled(circuitBreakerGroupEnabled)
.circuitBreakerNameResolver(circuitBreakerNameResolver);
}
}
FeignCircuitBreaker.Builder
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
public final class FeignCircuitBreaker {
......
/**
* Builder for Feign CircuitBreaker integration.
*/
public static final class Builder extends Feign.Builder {
private CircuitBreakerFactory circuitBreakerFactory;
private String feignClientName;
private boolean circuitBreakerGroupEnabled;
private CircuitBreakerNameResolver circuitBreakerNameResolver;
......
public <T> T target(Target<T> target, T fallback) {
//fallback使用FallbackFactory.Default包装后build创建Feign,然后使用newInstance获取FeignClient代理对象
return build(fallback != null ? new FallbackFactory.Default<T>(fallback) : null).newInstance(target);
}
public <T> T target(Target<T> target, FallbackFactory<? extends T> fallbackFactory) {
return build(fallbackFactory).newInstance(target);
}
@Override
public <T> T target(Target<T> target) {
return build(null).newInstance(target);
}
public Feign build(final FallbackFactory<?> nullableFallbackFactory) {
//fallback配置 invocationHandlerFactory
//invocationHandlerFactory创建的InvocationHandler是FeignCircuitBreakerInvocationHandler
super.invocationHandlerFactory((target, dispatch) -> new FeignCircuitBreakerInvocationHandler(
circuitBreakerFactory, feignClientName, target, dispatch, nullableFallbackFactory,
circuitBreakerGroupEnabled, circuitBreakerNameResolver));
//最后调用父类,也就是Feign.Builder#build()方法创建Feign
return super.build();
}
}
}
InvocationHandlerFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public interface InvocationHandlerFactory {
//@param target 记录了 FeignClient的信息,具体实现HardCodedTarget
//@param dispatch 方法 -> MethodHandler Map
InvocationHandler create(Target target, Map<Method, MethodHandler> dispatch);
/**
* Like {@link InvocationHandler#invoke(Object, java.lang.reflect.Method, Object[])}, except for a
* single method.
*/
//FeignClient代理类invoke后使用MethodHandler执行http调用,具体见执行的时候
interface MethodHandler {
Object invoke(Object[] argv) throws Throwable;
}
static final class Default implements InvocationHandlerFactory {
@Override
public InvocationHandler create(Target target, Map<Method, MethodHandler> dispatch) {
return new ReflectiveFeign.FeignInvocationHandler(target, dispatch);
}
}
}
FeignClient 执行
Feign执行是通过动态代理类实现的,具体的代码见invoke方法
-
无断路:
ReflectiveFeign.FeignInvocationHandler -
断路:
FeignCircuitBreakerInvocationHandler(或第三方实现的)
FeignCircuitBreakerInvocationHandler
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
class FeignCircuitBreakerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final CircuitBreakerFactory factory;
private final String feignClientName;
private final Target<?> target;
private final Map<Method, InvocationHandlerFactory.MethodHandler> dispatch;
private final FallbackFactory<?> nullableFallbackFactory;
private final Map<Method, Method> fallbackMethodMap;
private final boolean circuitBreakerGroupEnabled;
private final CircuitBreakerNameResolver circuitBreakerNameResolver;
......
@Override
public Object invoke(final Object proxy, final Method method, final Object[] args) throws Throwable {
......
String circuitName = circuitBreakerNameResolver.resolveCircuitBreakerName(feignClientName, target, method);
//使用CircuitBreakerFactory获取CircuitBreaker,都是接口
CircuitBreaker circuitBreaker = circuitBreakerGroupEnabled ? factory.create(circuitName, feignClientName)
: factory.create(circuitName);
//将方法的执行包装为supplier
Supplier<Object> supplier = asSupplier(method, args);
if (this.nullableFallbackFactory != null) {
//断路执行包装为function
Function<Throwable, Object> fallbackFunction = throwable -> {
Object fallback = this.nullableFallbackFactory.create(throwable);
try {
return this.fallbackMethodMap.get(method).invoke(fallback, args);
}
catch (Exception exception) {
unwrapAndRethrow(exception);
}
return null;
};
//交由CircuitBreaker执行
return circuitBreaker.run(supplier, fallbackFunction);
}
return circuitBreaker.run(supplier);
}
private void unwrapAndRethrow(Exception exception) {
if (exception instanceof InvocationTargetException || exception instanceof NoFallbackAvailableException) {
Throwable underlyingException = exception.getCause();
if (underlyingException instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) underlyingException;
}
if (underlyingException != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(underlyingException);
}
throw new IllegalStateException(exception);
}
}
private Supplier<Object> asSupplier(final Method method, final Object[] args) {
final RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
return () -> {
try {
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes);
//获取MethodHandler执行具体方法,也即http调用
return dispatch.get(method).invoke(args);
}
catch (RuntimeException throwable) {
throw throwable;
}
catch (Throwable throwable) {
throw new RuntimeException(throwable);
}
};
}
......
}
SynchronousMethodHandler
MethodHandler实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
final class SynchronousMethodHandler implements MethodHandler {
private static final long MAX_RESPONSE_BUFFER_SIZE = 8192L;
private final MethodMetadata metadata;
private final Target<?> target;
private final Client client;
private final Retryer retryer;
private final List<RequestInterceptor> requestInterceptors;
private final Logger logger;
private final Logger.Level logLevel;
private final RequestTemplate.Factory buildTemplateFromArgs;
private final Options options;
private final ExceptionPropagationPolicy propagationPolicy;
// only one of decoder and asyncResponseHandler will be non-null
private final Decoder decoder;
private final AsyncResponseHandler asyncResponseHandler;
......
@Override
public Object invoke(Object[] argv) throws Throwable {
RequestTemplate template = buildTemplateFromArgs.create(argv);
Options options = findOptions(argv);
Retryer retryer = this.retryer.clone();
while (true) {
try {
return executeAndDecode(template, options);
} catch (RetryableException e) {
try {
retryer.continueOrPropagate(e);
} catch (RetryableException th) {
Throwable cause = th.getCause();
if (propagationPolicy == UNWRAP && cause != null) {
throw cause;
} else {
throw th;
}
}
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logRetry(metadata.configKey(), logLevel);
}
continue;
}
}
}
Object executeAndDecode(RequestTemplate template, Options options) throws Throwable {
//创建feign request
Request request = targetRequest(template);
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logRequest(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, request);
}
Response response;
long start = System.nanoTime();
try {
//client 执行http请求
response = client.execute(request, options);
// ensure the request is set. TODO: remove in Feign 12
response = response.toBuilder()
.request(request)
.requestTemplate(template)
.build();
} catch (IOException e) {
if (logLevel != Logger.Level.NONE) {
logger.logIOException(metadata.configKey(), logLevel, e, elapsedTime(start));
}
throw errorExecuting(request, e);
}
long elapsedTime = TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - start);
if (decoder != null)
return decoder.decode(response, metadata.returnType());
CompletableFuture<Object> resultFuture = new CompletableFuture<>();
asyncResponseHandler.handleResponse(resultFuture, metadata.configKey(), response,
metadata.returnType(),
elapsedTime);
try {
if (!resultFuture.isDone())
throw new IllegalStateException("Response handling not done");
return resultFuture.join();
} catch (CompletionException e) {
Throwable cause = e.getCause();
if (cause != null)
throw cause;
throw e;
}
}
......
Request targetRequest(RequestTemplate template) {
//feign RequestInterceptor执行
for (RequestInterceptor interceptor : requestInterceptors) {
interceptor.apply(template);
}
return target.apply(template);
}
......
}
Client
Feign Client 负责具体的http调用
-
FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient:结合Spring Cloud loadbalance实现负载均衡,使用
LoadBalancerClient实现负载均衡 -
RetryableFeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient:Spring Cloud loadbalance实现负载均衡、Spring Retry实现重试,
RetryTemplate实现重试 -
DefaultFeignLoadBalancerConfiguration:默认Feign Client注入
-
OkHttpFeignLoadBalancerConfiguration:OKHttp Client注入
-
HttpClientFeignLoadBalancerConfiguration:Apache Http Client注入
-
HttpClient5FeignLoadBalancerConfiguration:Apache Http5 Client注入
其中FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient、RetryableFeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient用代理模式实现,只是负责负载均衡&重试,真正的Http Client得看注入的delegate,这就跟FeignClientFactoryBean注入Client对应上了