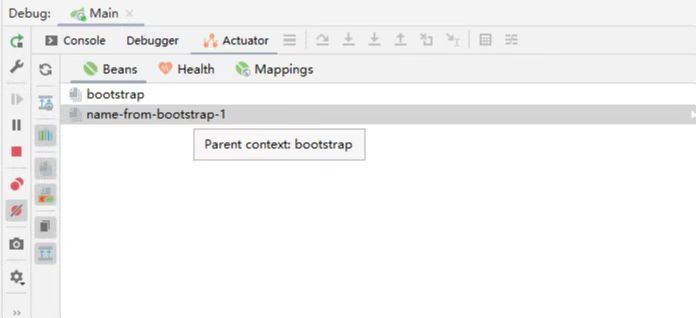
在使用Spring Cloud 的情况下,通常使用的配置文件为bootstrap.yaml,而这需要引入 spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap才能生效,同时在引入spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap的情况下,观察Spring Context会发现,多了一个名为bootstrap的Parent Context。
So,今天就来分析一下spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap干了啥子。
Demo
pom.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
<spring-boot.version>2.6.2</spring-boot.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2021.0.2</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Main.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
@SpringBootApplication
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Main.class, args);
}
}
bootstrap.yaml
1
2
3
spring:
application:
name: name-from-bootstrap
一顿分析
先看spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap,发现它跟别的starter不太一样,别的都是只有引入一些依赖,而它多了一个标记类,根据注释这个类的作用跟配置了spring.cloud.bootstrap.enabled=true一样。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
package org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.marker;
/**
* A marker class, so that, if present, spring cloud bootstrap is enable similar to how
* 'spring.cloud.bootstrap.enabled=true' works.
*/
public abstract class Marker {
private Marker() {
}
}
接着看它用在了哪里,发现在spring-cloud-context下的自动装配配置spring-autoconfigure-metadata.properties中有
1
2
3
4
5
......
org.springframework.cloud.util.ConditionalOnBootstrapDisabled$OnBootstrapDisabledCondition$OnBootstrapMarkerClassPresent=
org.springframework.cloud.util.ConditionalOnBootstrapDisabled$OnBootstrapDisabledCondition$OnBootstrapMarkerClassPresent.ConditionalOnClass=org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.marker.Marker
org.springframework.cloud.util.ConditionalOnBootstrapEnabled$OnBootstrapEnabledCondition$OnBootstrapMarkerClassPresent=
org.springframework.cloud.util.ConditionalOnBootstrapEnabled$OnBootstrapEnabledCondition$OnBootstrapMarkerClassPresent.ConditionalOnClass=org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.marker.Marker
接着看@ConditionalOnBootstrapDisabled和@ConditionalOnBootstrapEnabled,发现只有RefreshAutoConfiguration用它们分别引入了ConfigDataContextRefresher和LegacyContextRefresher,虽然这两个类与配置有关,但主要是刷新配置相关的,可以先放一放。
就在此次线索中断的时候,通过@ConditionalOnBootstrapEnabled发现spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap中的Marker类名作为一个常量在PropertyUtils中,同时还有一个boolean变量MARKER_CLASS_EXISTS以及一个bootstrapEnabled方法。(什么叫柳暗花明又一村啊,又一村)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
package org.springframework.cloud.util;
.....
public abstract class PropertyUtils {
/**
* Property name for checking if bootstrap is enabled.
*/
public static final String BOOTSTRAP_ENABLED_PROPERTY = "spring.cloud.bootstrap.enabled";
/**
* Property name for spring boot legacy processing.
*/
public static final String USE_LEGACY_PROCESSING_PROPERTY = "spring.config.use-legacy-processing";
/**
* Property name for bootstrap marker class name.
*/
public static final String MARKER_CLASS = "org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.marker.Marker";
/**
* Boolean if bootstrap marker class exists.
*/
public static final boolean MARKER_CLASS_EXISTS = ClassUtils.isPresent(MARKER_CLASS, null);
......
public static boolean bootstrapEnabled(Environment environment) {
return environment.getProperty(BOOTSTRAP_ENABLED_PROPERTY, Boolean.class, false) || MARKER_CLASS_EXISTS;
}
public static boolean useLegacyProcessing(Environment environment) {
return environment.getProperty(USE_LEGACY_PROCESSING_PROPERTY, Boolean.class, false);
}
}
查看bootstrapEnabled方法的调用,会发现最可疑的就是BootstrapApplicationListener,仔细观察,加上debug的方式最终锁定他就是关键啦,接下来就回到正常的分析吧。。。
BootstrapApplicationListener
前置知识:
Spring Boot 启动过程加载ApplicationListener
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
//在SpringApplication构造方法中会通过SpringFactoriesLoader获取ApplicationListener
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList<>(
getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class));
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//这里
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
1
2
3
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapApplicationListener,\
Spring Boot 启动过程发布 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
1
SpringApplication#run -> prepareEnvironment -> SpringApplicationRunListeners#environmentPrepared -> EventPublishingRunListener#evironmentPrepared
开始分析,BootstrapApplicationListener本身就是ApplicationListener,同时在spring-cloud-context中有配置,所以会被加载进去。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
public class BootstrapApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent>, Ordered {
/**
* Property source name for bootstrap.
*/
public static final String BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "bootstrap";
/**
* The default order for this listener.
*/
public static final int DEFAULT_ORDER = Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 5;
/**
* The name of the default properties.
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_PROPERTIES = "springCloudDefaultProperties";
private int order = DEFAULT_ORDER;
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();
//这里会判断是否启用bootstrap,就是看有没有引入spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap,或者别的(略)
if (!bootstrapEnabled(environment) && !useLegacyProcessing(environment)) {
return;
}
// don't listen to events in a bootstrap context
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) {
return;
}
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
String configName = environment.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.name:bootstrap}");
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<?> initializer : event.getSpringApplication().getInitializers()) {
if (initializer instanceof ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer) {
//根据ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer查找,不是重点
context = findBootstrapContext((ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer) initializer, configName);
}
}
//这里才是重点
if (context == null) {
context = bootstrapServiceContext(environment, event.getSpringApplication(), configName);
event.getSpringApplication().addListeners(new CloseContextOnFailureApplicationListener(context));
}
apply(context, event.getSpringApplication(), environment);
}
......
//这个方法比较长,不过没关系,挑重点看
private ConfigurableApplicationContext bootstrapServiceContext(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
final SpringApplication application, String configName) {
ConfigurableEnvironment bootstrapEnvironment = new AbstractEnvironment() {
};
MutablePropertySources bootstrapProperties = bootstrapEnvironment.getPropertySources();
String configLocation = environment.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.location:}");
String configAdditionalLocation = environment
.resolvePlaceholders("${spring.cloud.bootstrap.additional-location:}");
Map<String, Object> bootstrapMap = new HashMap<>();
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.name", configName);
// if an app (or test) uses spring.main.web-application-type=reactive, bootstrap
// will fail
// force the environment to use none, because if though it is set below in the
// builder
// the environment overrides it
bootstrapMap.put("spring.main.web-application-type", "none");
if (StringUtils.hasText(configLocation)) {
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.location", configLocation);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(configAdditionalLocation)) {
bootstrapMap.put("spring.config.additional-location", configAdditionalLocation);
}
bootstrapProperties.addFirst(new MapPropertySource(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, bootstrapMap));
for (PropertySource<?> source : environment.getPropertySources()) {
if (source instanceof StubPropertySource) {
continue;
}
bootstrapProperties.addLast(source);
}
// TODO: is it possible or sensible to share a ResourceLoader?
SpringApplicationBuilder builder = new SpringApplicationBuilder().profiles(environment.getActiveProfiles())
.bannerMode(Mode.OFF).environment(bootstrapEnvironment)
// Don't use the default properties in this builder
.registerShutdownHook(false).logStartupInfo(false).web(WebApplicationType.NONE);
final SpringApplication builderApplication = builder.application();
if (builderApplication.getMainApplicationClass() == null) {
// gh_425:
// SpringApplication cannot deduce the MainApplicationClass here
// if it is booted from SpringBootServletInitializer due to the
// absense of the "main" method in stackTraces.
// But luckily this method's second parameter "application" here
// carries the real MainApplicationClass which has been explicitly
// set by SpringBootServletInitializer itself already.
builder.main(application.getMainApplicationClass());
}
if (environment.getPropertySources().contains("refreshArgs")) {
// If we are doing a context refresh, really we only want to refresh the
// Environment, and there are some toxic listeners (like the
// LoggingApplicationListener) that affect global static state, so we need a
// way to switch those off.
builderApplication.setListeners(filterListeners(builderApplication.getListeners()));
}
//重点,加入BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration,这个类是bootstrap 配置能生效的原因
builder.sources(BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration.class);
//使用SpringApplicationBuilder创建了bootstrap 的context
final ConfigurableApplicationContext context = builder.run();
// gh-214 using spring.application.name=bootstrap to set the context id via
// `ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer` prevents apps from getting the actual
// spring.application.name
// during the bootstrap phase.
context.setId("bootstrap");
// Make the bootstrap context a parent of the app context
//这个比较重要,是bootstrap context 和 applicaion context 关联有关
addAncestorInitializer(application, context);
// It only has properties in it now that we don't want in the parent so remove
// it (and it will be added back later)
bootstrapProperties.remove(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
mergeDefaultProperties(environment.getPropertySources(), bootstrapProperties);
return context;
}
......
private void addAncestorInitializer(SpringApplication application, ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
//将context作为parent创建AncestorInitializer并添加到SpringApplication中
boolean installed = false;
for (ApplicationContextInitializer<?> initializer : application.getInitializers()) {
if (initializer instanceof AncestorInitializer) {
installed = true;
// New parent
((AncestorInitializer) initializer).setParent(context);
}
}
if (!installed) {
application.addInitializers(new AncestorInitializer(context));
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void apply(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, SpringApplication application,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
//BootstrapMarkerConfiguration,又是一个标记类,大致上是配置过的不配置了
if (application.getAllSources().contains(BootstrapMarkerConfiguration.class)) {
return;
}
application.addPrimarySources(Arrays.asList(BootstrapMarkerConfiguration.class));
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
Set target = new LinkedHashSet<>(application.getInitializers());
//主要是获取bootstrap context 中的ApplicationContextInitializer添加到SpringApplication中
target.addAll(getOrderedBeansOfType(context, ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
application.setInitializers(target);
addBootstrapDecryptInitializer(application);
}
......
private static class AncestorInitializer
implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered {
private ConfigurableApplicationContext parent;
......
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
while (context.getParent() != null && context.getParent() != context) {
context = (ConfigurableApplicationContext) context.getParent();
}
reorderSources(context.getEnvironment());
//其实主要是存放了bootstrap context,具体关联的动作在ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer
new ParentContextApplicationContextInitializer(this.parent).initialize(context);
}
......
}
......
}
简单的来讲,BootstrapApplicationListener的主要作用是往SpringApplication中添加了BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration以及ApplicationContextInitializer。
挑重点看BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration,就是引入了BootstrapImportSelector。
BootstrapImportSelector
这个类的作用就更简单了,主要就是用SpringFactoriesLoader扫描spring.factories中org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration配置的类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
public class BootstrapImportSelector implements EnvironmentAware, DeferredImportSelector {
private Environment environment;
private MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory();
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
//重点
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(BootstrapConfiguration.class, classLoader));
names.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils
.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(this.environment.getProperty("spring.cloud.bootstrap.sources", ""))));
List<OrderedAnnotatedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : names) {
try {
elements.add(new OrderedAnnotatedElement(this.metadataReaderFactory, name));
}
catch (IOException e) {
continue;
}
}
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(elements);
String[] classNames = elements.stream().map(e -> e.name).toArray(String[]::new);
return classNames;
}
......
}
看看都导入了啥类,在spring-cloud-context包的META-INF中,导入了以下类。
# Spring Cloud Bootstrap components
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config.PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration,\
org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.encrypt.EncryptionBootstrapConfiguration,\ #加密相关,过
org.springframework.cloud.autoconfigure.ConfigurationPropertiesRebinderAutoConfiguration,\ #配置重新绑定相关,@RefreshScope&JMX, 过
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration #配置占位符相关,过
看起来只剩下一个了。
PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration
可以看到PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration也是一个ApplicationContextInitializer,内部注入了PropertySourceLocator集合来获取各种形式的PropertySource。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(PropertySourceBootstrapProperties.class)
public class PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration
implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered {
......
@Autowired(required = false)
private List<PropertySourceLocator> propertySourceLocators = new ArrayList<>();
public void setPropertySourceLocators(Collection<PropertySourceLocator> propertySourceLocators) {
this.propertySourceLocators = new ArrayList<>(propertySourceLocators);
}
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
List<PropertySource<?>> composite = new ArrayList<>();
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.propertySourceLocators);
boolean empty = true;
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment();
//循环收集PropertySource
for (PropertySourceLocator locator : this.propertySourceLocators) {
Collection<PropertySource<?>> source = locator.locateCollection(environment);
if (source == null || source.size() == 0) {
continue;
}
List<PropertySource<?>> sourceList = new ArrayList<>();
for (PropertySource<?> p : source) {
if (p instanceof EnumerablePropertySource) {
EnumerablePropertySource<?> enumerable = (EnumerablePropertySource<?>) p;
sourceList.add(new BootstrapPropertySource<>(enumerable));
}
else {
sourceList.add(new SimpleBootstrapPropertySource(p));
}
}
logger.info("Located property source: " + sourceList);
composite.addAll(sourceList);
empty = false;
}
if (!empty) {
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
String logConfig = environment.resolvePlaceholders("${logging.config:}");
LogFile logFile = LogFile.get(environment);
for (PropertySource<?> p : environment.getPropertySources()) {
if (p.getName().startsWith(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) {
propertySources.remove(p.getName());
}
}
//将获取到的PropertySource集合放入ConfigurableEnvironment#MutablePropertySources中
insertPropertySources(propertySources, composite);
reinitializeLoggingSystem(environment, logConfig, logFile);
setLogLevels(applicationContext, environment);
handleIncludedProfiles(environment);
}
}
......
}
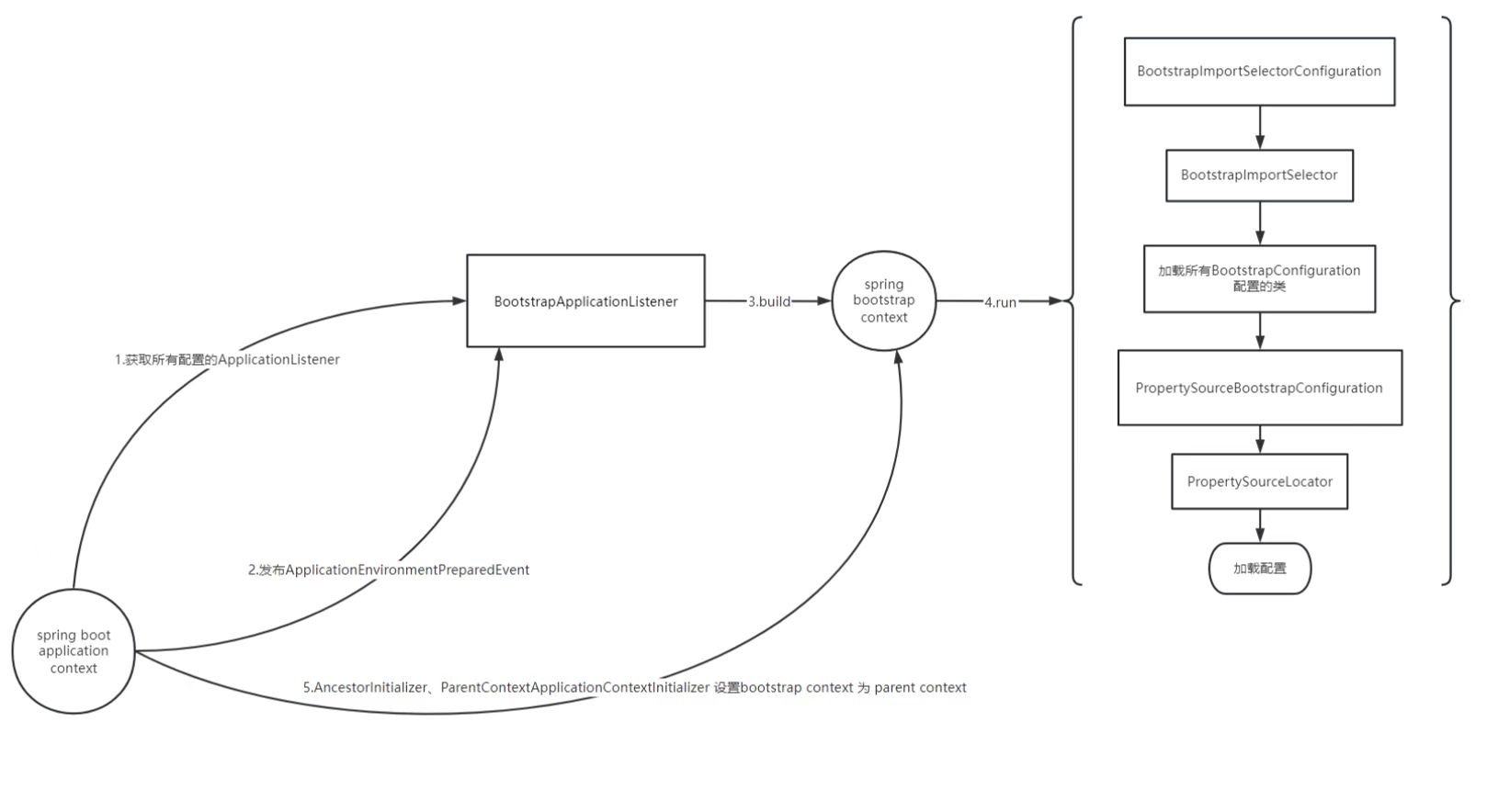
一图总结
References
-
Previous
static 影响 @Bean 与 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 分析 -
Next
spring cloud alibaba nacos config 配置加载&刷新流程