Spring Scope 工作流程
demo
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@Configuration
@RequestScope
//@RequestScope(proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.NO)
public class DynamicValueHolder {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DynamicValueHolder.class);
public DynamicValueHolder() {
logger.info("DynamicValueHolder create {}", this.hashCode());
}
@Value("${dynamic.value}")
private String value = "scope";
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
@RestController
@RequestMapping("dynamic")
public class DynamicValueController {
private DynamicValueHolder holder;
@Autowired
public void setHolder(DynamicValueHolder holder) {
this.holder = holder;
}
@GetMapping
public String get() {
return holder.hashCode() + " " + holder.getValue();
}
}
观察demo 的执行结果会有助于接下来的分析哦,可以看到返回的holder 的hashCode 都是同一个,但是每个请求都会触发DynamicValueHolder的创建,按道理应该不同才对呀。
剧透,这是因为controller 中注入的holder是一个代理对象,其它的看后文吧~~~
一图流 ~ ~ ~
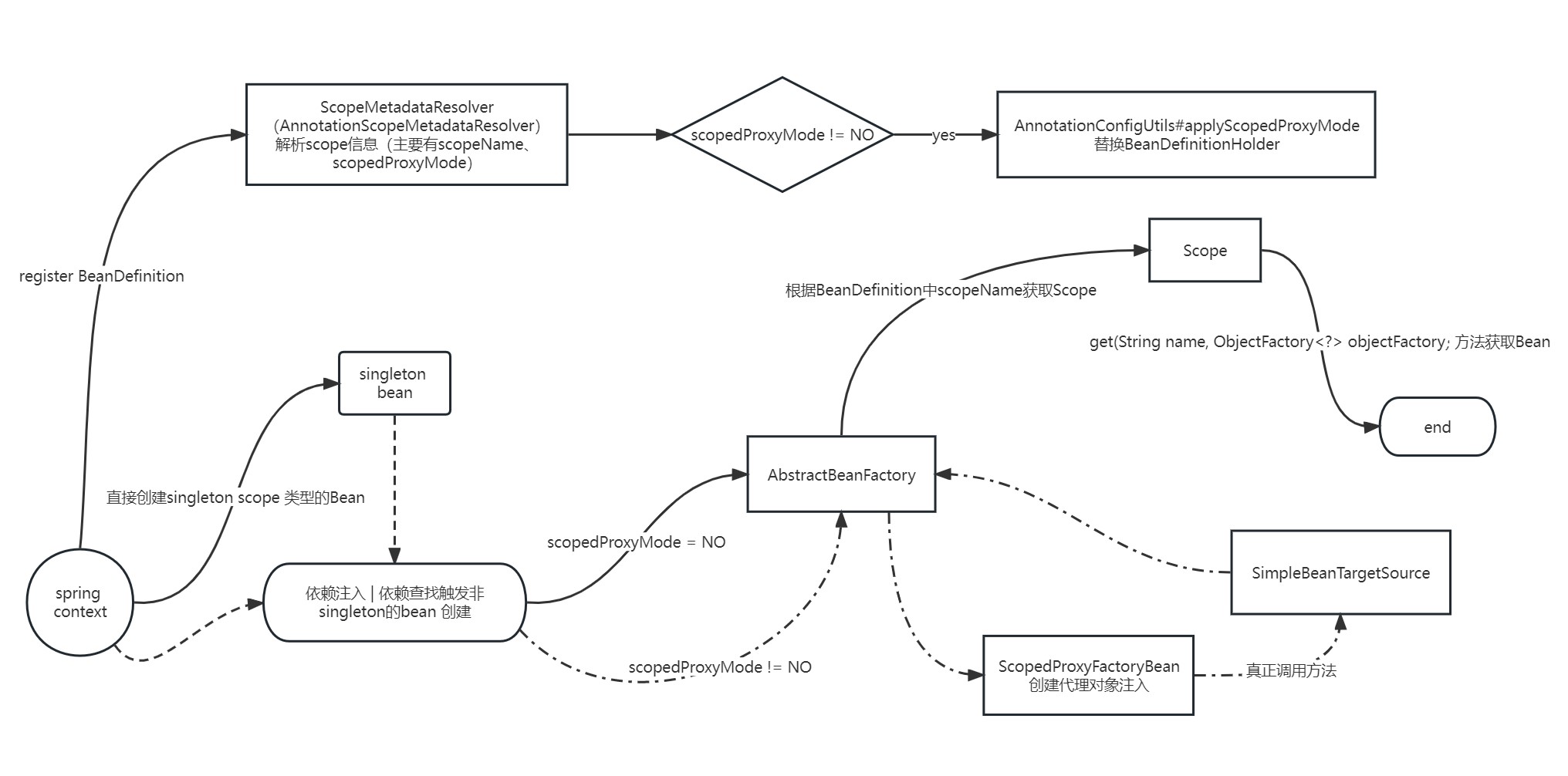
说明
- 在Spring Context 扫描
BeanDefinition过程中,会使用ScopeMetadataResolver(我想大家主要是通过Spring 标准注解吧,那么主要就是AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver这个实现类了),解析出ScopeMetadata(包括scopeName和scopedProxyMode)- 如果
scopedProxyMode不为NO,则为需要代理(INTERFACES表示 JDK动态代理,TARGET_CLASS表示CGLIB动态代理),此时会用AnnotationConfigUtils#applyScopedProxyMode替换BeanDefinitionHolder,而这个新的BeanDefinitionHolder有什么道道,后面再说~~ (见重点分析ScopedProxyUtils)
- 如果
- 在singleton类型的Bean创建,或后面应用运行过程中,发生依赖注入或依赖查找的情况下,触发其它Scope类型的Bean创建
- 对于
scopedProxyMode == NO的Bean来说,主要在AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean(String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)中,会根据BeanDefinition中的scopeName获取对应的Scope,然后用Scope#get获取Bean。 - 对于
scopedProxyMode != NO的,会通过ScopedProxyFactoryBean创建一个代理对象返回,在真正发生方法调用时,通过SimpleBeanTargetSource触发Bean的创建(创建的过程就和scopedProxyMode == NO的Bean一样)。为什么要用代理,其实很简单,主要是为了依赖注入,通过一个中间的代理类可以使非singleton的Bean的难度降低很多(试想注入了一个Bean,后续需要替换它你会怎么做),可以试试demo 替换@RequestScope(proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.NO)。
- 对于
重点分析
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
注册BeanDefinition,除了ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner外,还有AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader、ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader,在Scope的处理上,都是差不多的逻辑
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
//解析ScopeMetadata信息
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
//BeanDefinitionHolder 处理,可能会被替换(替换成ScopedProxyFactoryBean的BeanDefinition)
definitionHolder =
AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
AnnotationConfigUtils
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
static BeanDefinitionHolder applyScopedProxyMode(
ScopeMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionHolder definition, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
ScopedProxyMode scopedProxyMode = metadata.getScopedProxyMode();
if (scopedProxyMode.equals(ScopedProxyMode.NO)) {
return definition;
}
//需要代理的情况替换BeanDefinitionHolder
boolean proxyTargetClass = scopedProxyMode.equals(ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS);
return ScopedProxyCreator.createScopedProxy(definition, registry, proxyTargetClass);
}
ScopedProxyUtils
需要代理的Bean的BeanDefinitionHolder 创建
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
public abstract class ScopedProxyUtils {
//scopedTarget前缀
private static final String TARGET_NAME_PREFIX = "scopedTarget.";
private static final int TARGET_NAME_PREFIX_LENGTH = TARGET_NAME_PREFIX.length();
/**
* Generate a scoped proxy for the supplied target bean, registering the target
* bean with an internal name and setting 'targetBeanName' on the scoped proxy.
* @param definition the original bean definition
* @param registry the bean definition registry
* @param proxyTargetClass whether to create a target class proxy
* @return the scoped proxy definition
* @see #getTargetBeanName(String)
* @see #getOriginalBeanName(String)
*/
public static BeanDefinitionHolder createScopedProxy(BeanDefinitionHolder definition,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, boolean proxyTargetClass) {
String originalBeanName = definition.getBeanName();
//原本的BeanDefinition 为targetDefinition
BeanDefinition targetDefinition = definition.getBeanDefinition();
//targetBeanName = scopedTarget.+ 原本的beanName
String targetBeanName = getTargetBeanName(originalBeanName);
// Create a scoped proxy definition for the original bean name,
// "hiding" the target bean in an internal target definition.
//创建一个类型为ScopedProxyFactoryBean 的 RootBeanDefinition,用于代理原本的Bean
RootBeanDefinition proxyDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(ScopedProxyFactoryBean.class);
//将targetBeanName + 原本的BeanDefintion 封装成BeanDefinitionHolder 写入 decoratedDefinition
proxyDefinition.setDecoratedDefinition(new BeanDefinitionHolder(targetDefinition, targetBeanName));
proxyDefinition.setOriginatingBeanDefinition(targetDefinition);
proxyDefinition.setSource(definition.getSource());
proxyDefinition.setRole(targetDefinition.getRole());
proxyDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("targetBeanName", targetBeanName);
if (proxyTargetClass) {
targetDefinition.setAttribute(AutoProxyUtils.PRESERVE_TARGET_CLASS_ATTRIBUTE, Boolean.TRUE);
// ScopedProxyFactoryBean's "proxyTargetClass" default is TRUE, so we don't need to set it explicitly here.
}
else {
proxyDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("proxyTargetClass", Boolean.FALSE);
}
// Copy autowire settings from original bean definition.
proxyDefinition.setAutowireCandidate(targetDefinition.isAutowireCandidate());
proxyDefinition.setPrimary(targetDefinition.isPrimary());
if (targetDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
proxyDefinition.copyQualifiersFrom((AbstractBeanDefinition) targetDefinition);
}
// The target bean should be ignored in favor of the scoped proxy.
targetDefinition.setAutowireCandidate(false);
targetDefinition.setPrimary(false);
// Register the target bean as separate bean in the factory.
//将targetBeanName + 原本的BeanDefintion 注册
registry.registerBeanDefinition(targetBeanName, targetDefinition);
// Return the scoped proxy definition as primary bean definition
// (potentially an inner bean).
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(proxyDefinition, originalBeanName, definition.getAliases());
}
/**
* Generate the bean name that is used within the scoped proxy to reference the target bean.
* @param originalBeanName the original name of bean
* @return the generated bean to be used to reference the target bean
* @see #getOriginalBeanName(String)
*/
public static String getTargetBeanName(String originalBeanName) {
return TARGET_NAME_PREFIX + originalBeanName;
}
......
}
这部分的逻辑光看代码会觉得乱,建议自己去Debug,这里放几张图辅助
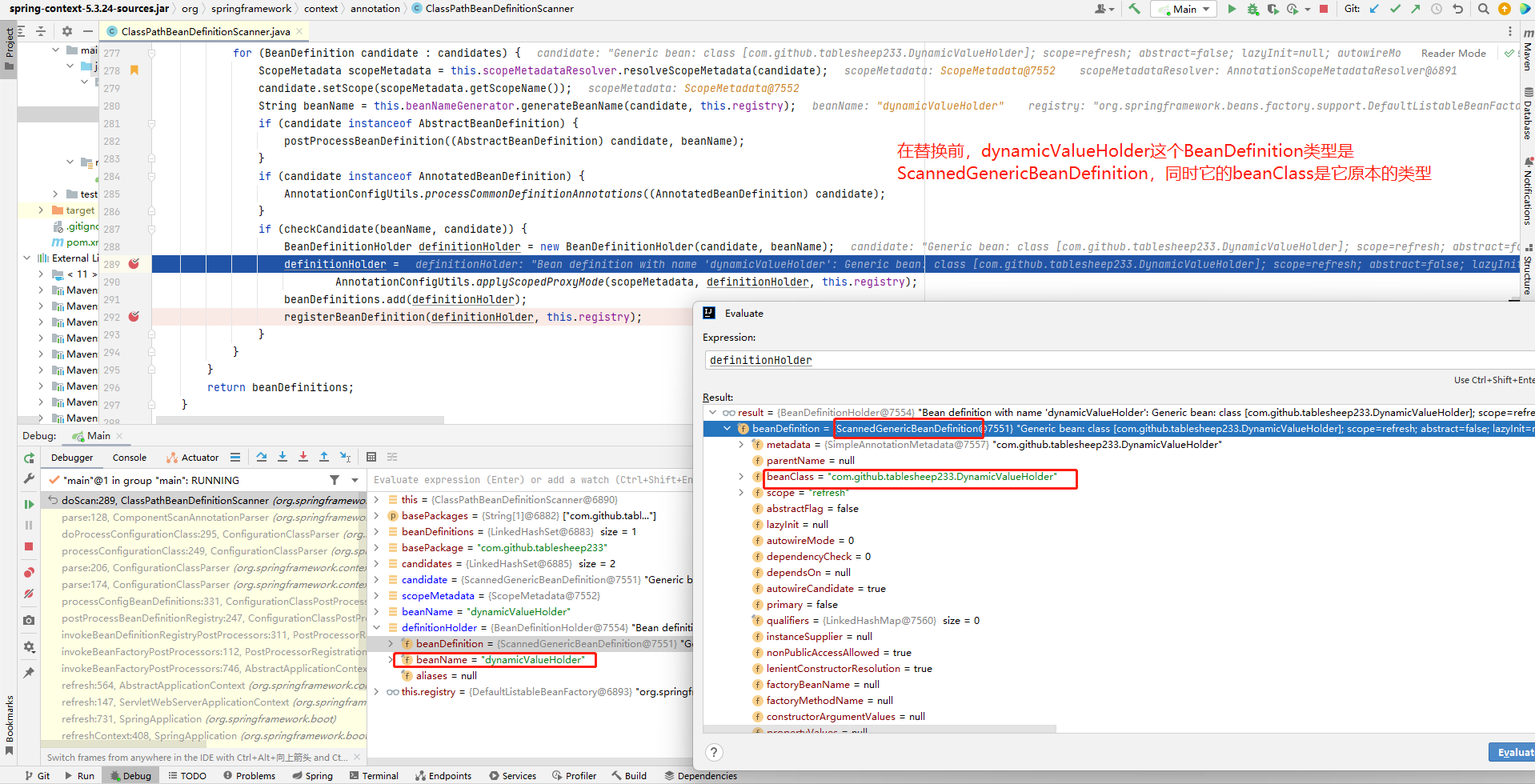
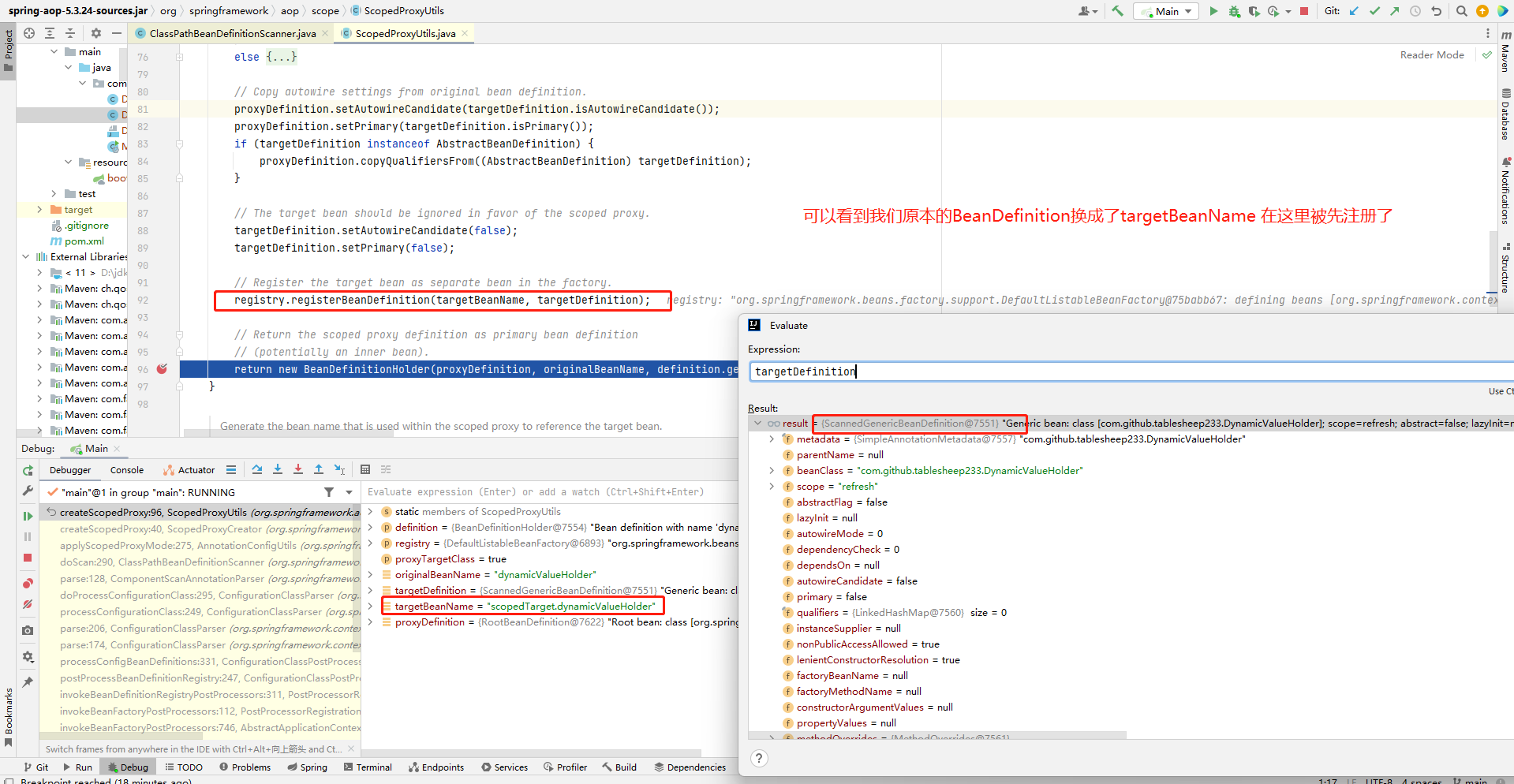
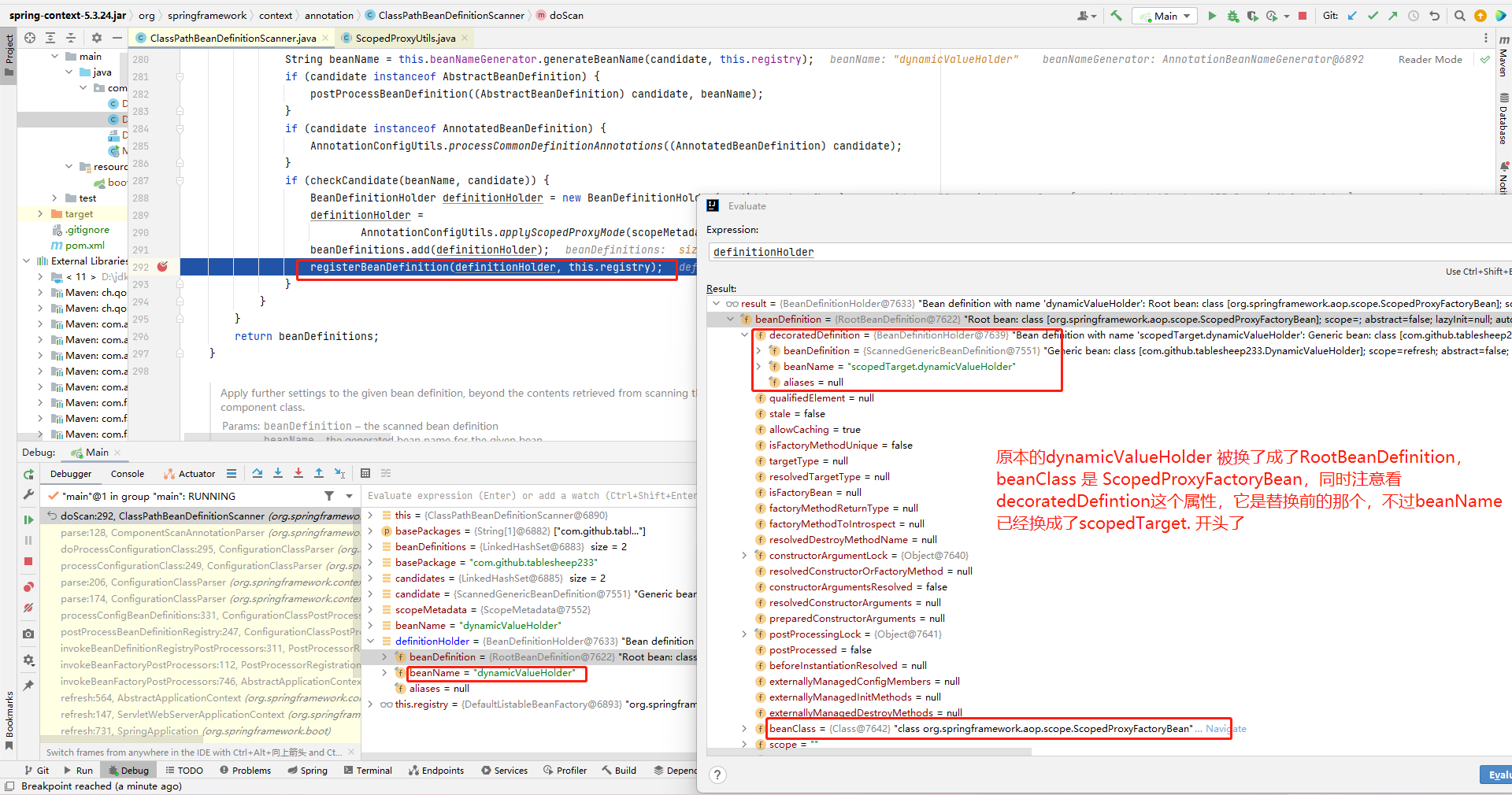
ScopedProxyFactoryBean
原本的Bean会通过ScopedProxyFactoryBean创建一个代理对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
public class ScopedProxyFactoryBean extends ProxyConfig
implements FactoryBean<Object>, BeanFactoryAware, AopInfrastructureBean {
/** The TargetSource that manages scoping. */
private final SimpleBeanTargetSource scopedTargetSource = new SimpleBeanTargetSource();
/** The name of the target bean. */
@Nullable
private String targetBeanName;
/** The cached singleton proxy. */
@Nullable
private Object proxy;
/**
* Create a new ScopedProxyFactoryBean instance.
*/
public ScopedProxyFactoryBean() {
setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
/**
* Set the name of the bean that is to be scoped.
*/
public void setTargetBeanName(String targetBeanName) {
this.targetBeanName = targetBeanName;
this.scopedTargetSource.setTargetBeanName(targetBeanName);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
if (!(beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Not running in a ConfigurableBeanFactory: " + beanFactory);
}
ConfigurableBeanFactory cbf = (ConfigurableBeanFactory) beanFactory;
this.scopedTargetSource.setBeanFactory(beanFactory);
ProxyFactory pf = new ProxyFactory();
pf.copyFrom(this);
pf.setTargetSource(this.scopedTargetSource);
Assert.notNull(this.targetBeanName, "Property 'targetBeanName' is required");
Class<?> beanType = beanFactory.getType(this.targetBeanName);
if (beanType == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot create scoped proxy for bean '" + this.targetBeanName +
"': Target type could not be determined at the time of proxy creation.");
}
if (!isProxyTargetClass() || beanType.isInterface() || Modifier.isPrivate(beanType.getModifiers())) {
pf.setInterfaces(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClass(beanType, cbf.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
// Add an introduction that implements only the methods on ScopedObject.
ScopedObject scopedObject = new DefaultScopedObject(cbf, this.scopedTargetSource.getTargetBeanName());
pf.addAdvice(new DelegatingIntroductionInterceptor(scopedObject));
// Add the AopInfrastructureBean marker to indicate that the scoped proxy
// itself is not subject to auto-proxying! Only its target bean is.
pf.addInterface(AopInfrastructureBean.class);
//关键在这里,创建代理对象
this.proxy = pf.getProxy(cbf.getBeanClassLoader());
}
@Override
public Object getObject() {
if (this.proxy == null) {
throw new FactoryBeanNotInitializedException();
}
return this.proxy;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
if (this.proxy != null) {
return this.proxy.getClass();
}
return this.scopedTargetSource.getTargetClass();
}
......
}
SimpleBeanTargetSource
原本的BeanName 的代理对象里的TargetSource,通过它获取真正需要的Bean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class SimpleBeanTargetSource extends AbstractBeanFactoryBasedTargetSource {
@Override
public Object getTarget() throws Exception {
//AbstractBeanFactoryBasedTargetSource里有一个BeanFactory,而targetBeanName 就是 scopedTarget. 开头 + 原本beanName
return getBeanFactory().getBean(getTargetBeanName());
}
}
AbstractBeanFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
protected <T> T doGetBean(
String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object beanInstance;
......
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(scopeName)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No scope name defined for bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
//从map中获取对应的Scope
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
//Scope#get 方法获取Bean
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
beanInstance = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new ScopeNotActiveException(beanName, scopeName, ex);
}
}
}
......
}
return adaptBeanInstance(name, beanInstance, requiredType);
}