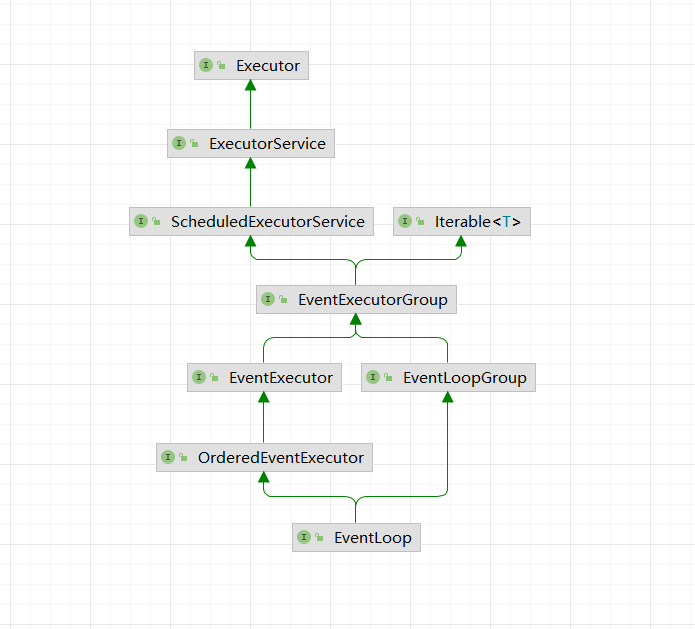
在看完了EventLoopGroup后,接着看具体工作的类EventLoop。
EventLoop
EventExecutor
EventLoop接口最主要的就是继承了EventExecutor,而EventExecutor则继承了EventExecutorGroup,同时扩展了一些方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
public interface EventExecutor extends EventExecutorGroup {
/**
* Returns a reference to itself.
* 返回自身
*/
@Override
EventExecutor next();
/**
* Return the {@link EventExecutorGroup} which is the parent of this {@link EventExecutor},
* 返回父EventExecutorGroup从这个方法可看出 EventExecutorGroup 跟 EventExecutor 是父子关系
* 就如 在 NioEventLoopGroup 中会创建多个 NioEventLoop一样
*/
EventExecutorGroup parent();
/**
* Calls {@link #inEventLoop(Thread)} with {@link Thread#currentThread()} as argument
*/
boolean inEventLoop();
/**
* Return {@code true} if the given {@link Thread} is executed in the event loop,
* {@code false} otherwise.
* 判断线程是否在 event loop (事件循环)中
*/
boolean inEventLoop(Thread thread);
/**
* Return a new {@link Promise}.
*/
<V> Promise<V> newPromise();
/**
* Create a new {@link ProgressivePromise}.
*/
<V> ProgressivePromise<V> newProgressivePromise();
/**
* Create a new {@link Future} which is marked as succeeded already. So {@link Future#isSuccess()}
* will return {@code true}. All {@link FutureListener} added to it will be notified directly. Also
* every call of blocking methods will just return without blocking.
*/
<V> Future<V> newSucceededFuture(V result);
/**
* Create a new {@link Future} which is marked as failed already. So {@link Future#isSuccess()}
* will return {@code false}. All {@link FutureListener} added to it will be notified directly. Also
* every call of blocking methods will just return without blocking.
*/
<V> Future<V> newFailedFuture(Throwable cause);
}
NioEventLoop
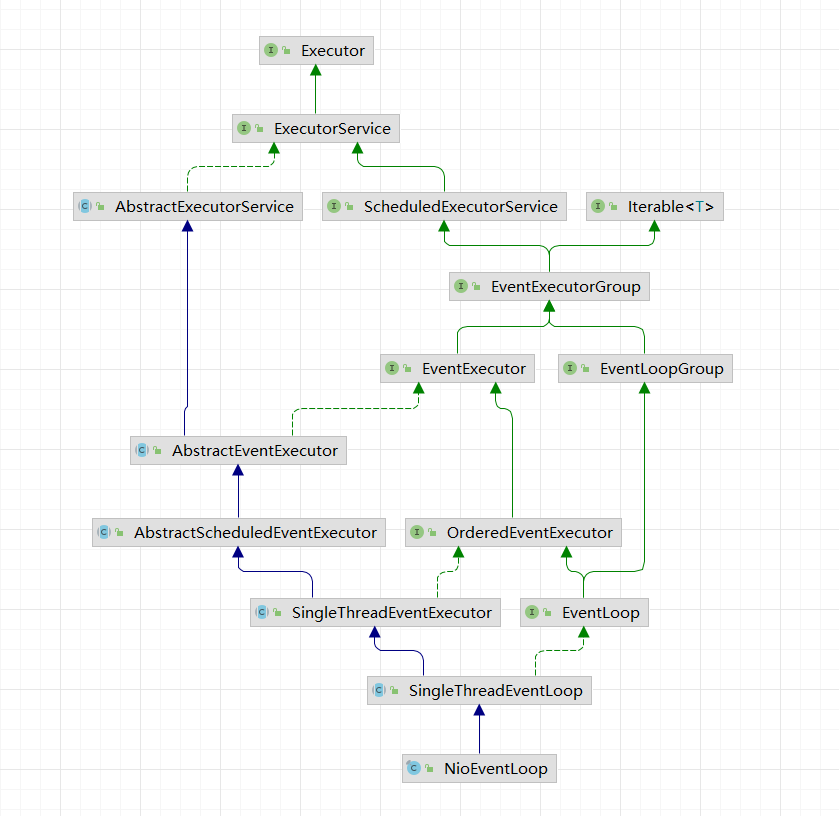
接着看NioEventLoop实现,还是自上而下
AbstractEventExecutor
AbstractEventExecutor主要实现了线程池的大部分方法以及EventExecutor的大部分方法(除了inEventLoop(Thread thread))
AbstractScheduledEventExecutor
AbstractScheduledEventExecutor扩展了AbstractEventExecutor,使其支持定时调度执行。
SingleThreadEventExecutor
使用单线程实现的EventExecutor,一个线程拥有一个独立的任务队列。
1
2
3
4
5
6
//重要的成员变量
private final Queue<Runnable> taskQueue; //线程队列
private volatile Thread thread; //执行event loop 的线程
private final Executor executor; //这个变量很有意思,就是靠它创建的线程
线程的启动
ThreadPerTaskExecutor
executor变量默认情况下是ThreadPerTaskExecutor(见MultithreadEventExecutorGroup构造方法)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public final class ThreadPerTaskExecutor implements Executor {
private final ThreadFactory threadFactory;
public ThreadPerTaskExecutor(ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
this.threadFactory = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(threadFactory, "threadFactory");
}
@Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
//使用线程工厂创建线程并启动
threadFactory.newThread(command).start();
}
}
SingleThreadEventExecutor#doStartThread
启动线程的方法,一开始看会觉得很绕,看懂了会觉得6。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
private void doStartThread() {
assert thread == null;
//当前线程为null,即未启动的情况下,使用executor去执行,而executor会创建一个新的线程去执行
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//而任务执行的第一步就是将当前线程(executor创建出来的那个)引用设置给 thread变量(EventLoop持有的线程)
thread = Thread.currentThread();
......
try {
//启动模板方法run()执行任务
SingleThreadEventExecutor.this.run();
success = true;
}
}
});
}
SingleThreadEventLoop
SingleThreadEventLoop主要是实现了EventLoopGroup中定义的register方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
@Override
public EventLoopGroup parent() {
return (EventLoopGroup) super.parent();
}
@Override
public EventLoop next() {
return (EventLoop) super.next();
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return register(new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, this));
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(final ChannelPromise promise) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(promise, "promise");
promise.channel().unsafe().register(this, promise);
return promise;
}
NioEventLoop
NioEventLoop实现了SingleThreadEventExecutor#run()方法,是整个事件循环具体执行内容的实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
@Override
protected void run() {
int selectCnt = 0;
for (;;) { //是一个无限的循环
//暂时略
.......
}
}